RESTON®STU – Shock Transmission Units
The mageba Shock Transmission Unit (STU) is designed to be connected between bridge structure components to form a rigid link under dynamic loads induced by forces such as vehicle braking and earthquakes. It can be used for strengthening of simple and continuous span bridges by distributing the acting horizontal loads (e.g. breaking forces) among all piers and abutments.
Media
Product Summary
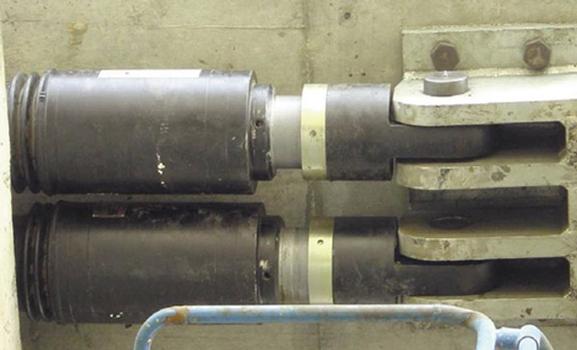
The mageba Shock Transmission Unit (STU) is designed to be connected between bridge structure components to form a rigid link under dynamic loads induced by forces such as vehicle braking and earthquakes. At the same time, the structure will be able to move freely under slowly applied loads such as temperature, creep and shrinkage.The unit is connected between elements of bridge structures at expansion joints, or near the bearings between the super-structure and the substructure. The use of STUs allows the load sharing of a suddenly applied force.
Design Principle
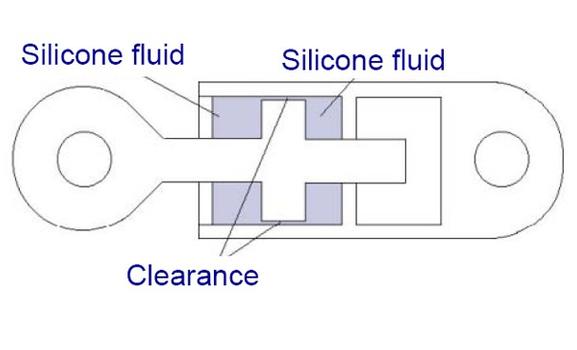
Shock Transmission Units work on the principle that rapid passage of a viscous fluid through a narrow gap, orifice or port generates high resistance, while slow passage at low velocity generates only minor resistance. An STU should block the deck of a bridge during a quick motion and behave like a spring with a very high stiffness. At the same time, the STU should deliver a low reaction force during the slow displacements of e.g. thermal expansion contraction of the deck.The mageba STU is made with a steel reservoir, with a piston rod sliding through it. On the piston rod, there is a fixed head, which in effect separates the reservoir into two chambers. When the unit is filled with silicone fluid, the pressure is the same in both chambers.
Anchoring System
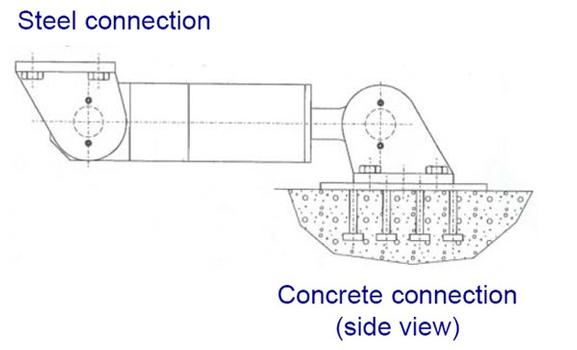
mageba Shock Transmission Unit (STU) can be delivered with the entire anchoring system. Depending on the bridge type, steel or concrete connections are required. The fixing from the STU to the connection base plate is made with bolts making the STU easily exchangeable.The rotational capacity between the STU and the support construction is guaranteed by the use of a high quality spherical plain bearing.
Common Applications
The mageba STU can be used for a wide range of applications. Following examples are most common applications:- Strengthening simple and continuous span bridges by distributing the acting horizontal loads (e.g. breaking forces) among all piers and abutments
- Connecting the pier of a cable stayed bridge with its deck, allowing free movements during normal operations and a rigid connection during seismic activities
- Retrofitting existing bridges at minimal costs where seismic up-grades are required
Materials
Following materials are used for the production of mageba STUs:- Main outer steel parts such as cylinder tubes, cylinder pipe, etc. made out of steel S355 according to DIN EN 10025-2
- Piston rod made out of steel 42CrMo4 according to DIN EN 10083-1
- Hydraulic valves made out of cast steel according to ISO 3755
Corrosion Protection
Corrosion protection according to DIN EN ISO 12944, C4ANV695, expected durability L (long). Target of surface roughness: Rz min 60µm, or alternatively Elcometer-roughness 2. Applied layers: Sand blasting Sa 2 ½, Zinc dust 2K-EP-primer 2-pack 50µm, MIO EP 2-pack 2x70µm, MIO-PUR, 2-pack 40µm. Total target thickness 230µm, Quality level 100% parts conform.Sealing
The sealing represents the most critical element of the total hydraulic system. Therefore, mageba employs a high grade sealing that demonstrates a quasi zero natural wear and an absolute physical-chemic compatibility with the adopted viscous fluid.Viscous Fluid
The mageba viscous fluid is based on a silicon oil with special additives, protecting it against natural aging and the STUs from inner corrosion. With respect to temperature variations, the viscosity of this selected fluid shows a nearly constant characteristic. This characteristic facilitates the mechanical system to be thermically compensated.Temperature and Aging
A variation of the outside temperature, which can range from -55°C to + 80°C, does not change the amount of energy dissipated per cycle. There is no aging of the silicone fluid. The mageba units have been tested in very severe environmental conditions, including fire.Testing
Full-scale testing can be carried out, if required. mageba performs its tests at a recognised independent test institute. Commonly used tests are:- Damping efficiency test to evaluate the energy dissipating capability
- Constitutive law test to determine the damper’s characteristic curve force vs. velocity
- Impressed low velocity test to evaluate the damper’s axial force resistance under simulated thermal movements






 mageba group
mageba group






