General Information
Project Type
| Function / usage: |
Theater building |
|---|---|
| Material: |
Reinforced concrete structure |
Awards and Distinctions
| 1977 |
for registered users |
|---|
Location
| Location: |
Tulle, Corrèze (19), Nouvelle-Aquitaine, France |
|---|---|
| Address: | Quai de la République |
| Coordinates: | 45° 16' 0.69" N 1° 46' 14.98" E |
Technical Information
Materials
| building structure |
reinforced cement
|
|---|
Excerpt from Wikipedia
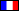
The Théâtre des Sept Collines (Theater of the Seven Hills) or Théâtre de Tulle is the municipal theater in the city of Tulle, Corrèze, France. It has an innovative reinforced concrete structure, the first such theater to be built. In 1932 it was converted into a cinema, but starting in 1994 was restored as a theater.
Origins
Tulle was served by a theater in part of the Abbey of Saint Martin for over sixty years until 1890, but the building had too many disadvantages to continue to be used for performances. The idea of building a new theater in Tulle is attributed to Jean-Baptiste Tavé (1856-1925), a lawyer and radical deputy. After being elected mayor of Tulle in 1892, he became committed to completing the project.
During a meeting of 30 November 1894, the municipal council of Tulle approved construction of a theater on the Quai de la République, on the Corrèze River. The new Théâtre de Tulle was built between 1899 and 1902 on the site formerly occupied by a 17th-century Jesuit chapel.
Construction
The architects were Joseph Auberty and Anatole de Baudot, architect of the recently built Lycée Edmond Perrier in Tulle. Anatole de Baudot was a believer in the school of rationalist architecture launched by his teacher, Eugène Viollet-le-Duc, whose influence he freely acknowledged. To avoid the risk of fire, De Baudot proposed an innovative structure using the Paul Cottancin's reinforced concrete construction method. This was the first theater to be built of reinforced cement.
The theater was an Italian-style room with three narrow balconies. There was an entrance hall, above which was a foyer. The facade was polychrome, incorporating sandstone, limestone, ceramics, colored glass and brick.
Later history
In 1932, the municipality decided to transform the theatre into a cinema. The Eden operated from 1934 to 1988. The Parisian architect Dubreuil removed the original three balconies to make room for two broader and deeper balconies. The original reinforced cement roof was covered in the classic slate roof that is seen today.
It was decided to convert the building back to ist original purpose, with the job assigned to the architects Larrouy, Sicre and Hervé David and the designer Bernard Guillaumot. The changes made to the interior in 1932 were removed. A new concrete structure was installed inside that matched the exterior of the building, which was unchanged since the time of Anatole de Baudot. The two balconies were modified to leave only one spanning the theater. The stage opening, which was 6 by 6 metres (20 by 20 ft) was increased to 11 by 8 metres (36 by 26 ft), with a depth of 13 metres (43 ft), allowing almost any type of show to be staged. The theater was renovated with financial assistance of 50% from the state and 30% from the region. It reopened in 1994.
Text imported from Wikipedia article "Théâtre des Sept Collines" and modified on July 23, 2019 according to the CC-BY-SA 4.0 International license.
Participants
Relevant Web Sites
Relevant Publications
- (1994): Le Théâtre de Tulle. Corrèze. Association Culture & Patrimoine en Limousin, Limoges (France).
- About this
data sheet - Structure-ID
20022535 - Published on:
07/08/2006 - Last updated on:
23/12/2017