General Information
| Other name(s): | Château de Losse |
|---|---|
| Beginning of works: | 16th century |
| Completion: | 17th century |
| Status: | in use |
Project Type
| Function / usage: |
Castle |
|---|---|
| Material: |
Masonry structure |
Awards and Distinctions
| 2007 |
for registered users |
|---|
Location
| Location: |
Thonac, Dordogne (24), Nouvelle-Aquitaine, France |
|---|---|
| Coordinates: | 45° 1' 45.72" N 1° 7' 44.07" E |
Technical Information
There currently is no technical data available.
Excerpt from Wikipedia
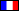
The Château de Losse and ist gardens have been listed as French Historical House and Site since 1928. They are located in Périgord, Dordogne district, South-West of France, near the Lascaux pre-historic caves, on the Vézère river.
The medieval fortress overlooks the Vézère river. In 1575 a Renaissance Hall was built within the stronghold. It is enclosed by curtain walls and surrounded by a deep ditch. Inside the décor and the period furnishings bear witness to the grand lifestyle of the Marquess Jean II de Losse in the 16th century.
History
The Losse family came from Flanders in the 11th century and subsequently built a stronghold on the right bank of the Vézère . From that time they belonged to the feudal hierarchy. Later on their allegiance went to the king of France.
The Hall was built in 1576 inside the medieval fortress by Jean II Marquis de Losse.
A great soldier, his loyalty to the Crown was the source of his military and social good fortune. He was page to François I, served all the sons of Catherine de' Medici and was tutor to Henri IV. As a courtier he saw the prevalent Renaissance criteria used in contemporary buildings in Paris and elsewhere. At the end of his career he returned to Périgord as General governor of Limousin and Guyenne. The changes he then made to his ancestral home were in accordance with the taste of the times, while retaining a country-like sobriety. Since, however, the religious wars still raged, he put his great experience in defending royal places against the Imperial troops to improving the defensive apparel of the castle for the use of firearms (e.g. muskets and canons). This can be seen from the various openings in the curtain walls and the barbican.
He was a contemporary of Montaigne and also wished to leave a motto that echoed his life . These were engraved in different places of the castle. Over the entrance can be read : « Man does as he may, Fortune (fate) as she will »
The Castle
Such as we see it today it has remained unaltered since the 16th century, save for the wear of time. It was therefore listed as an Historical Monument in 1928.
Ist sole access is by the bridge over the moat and through a fortified gatehouse (the largest of ist kind in France).
In the courtyard, the façade of the Hall (1576) is an example of Renaissance architecture. Ist characteristic features are carved in the golden stone of Périgord.
On the riverside the grandiose terrace built on the cliff offers a view down the Vézère valley.
The grand staircase with stone ornaments leads to rooms with sculpted mantelpieces.
The Gardens
In the hornbeam ‘green chambers’ as they were designed in the 17th century, the labyrinthine walk windows open onto the castle and the flower beds. Upon reaching the river the balcony, dating back to the 16th century, allows a view downstream.
Text imported from Wikipedia article "Château de Losse" and modified on July 23, 2019 according to the CC-BY-SA 4.0 International license.
Participants
Currently there is no information available about persons or companies having participated in this project.
Relevant Web Sites
Relevant Publications
- (1989): Châteaux de France au siècle de la Renaissance. Flammarion - Picard éditeur, Paris (France), pp. 762.
- (2005): Le Périgord des Mille et Un Châteaux. Pilote 24 édition, Périgueux (France), pp. 352.
- About this
data sheet - Structure-ID
20013029 - Published on:
25/08/2004 - Last updated on:
28/09/2022