General Information
Project Type
| Structure: |
Rockfill dam |
|---|---|
| Function / usage: |
Hydroelectric dam / plant |
Location
| Location: |
Vaujany, Isère (38), Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, France |
|---|---|
| Impounds: |
|
| Coordinates: | 45° 12' 21.56" N 6° 7' 3.14" E |
Technical Information
Dimensions
| height | 140.00 m | |
| retained water volume | 137.00 hm³ | |
| crest length | 550.00 m | |
| crest thickness | 10.00 m | |
| base thickness | 520.00 m |
Quantities
| dam-fill volume | 12 400 000 m³ |
Chronology
| 1988 | Dam enters into service. |
|---|
Excerpt from Wikipedia
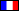
The Grand'Maison Dam is an embankment dam on L'Eau d'Olle, a tributary of the Romanche River. It is located in Vaujany of Isère within the French Alps. The primary purpose of the dam is to serve as the upper reservoir for a pumped-storage hydroelectric scheme where Lac du Verney located lower in the valley is the lower reservoir. The dam was constructed between 1978 and 1985 with its power station being commissioned in 1987. With an installed capacity of 1,800 MW, it is the largest hydroelectric power station in France.
Design and operation
The Grand'Maison is an embankment dam with a height of 140 m (459 ft) from the riverbed and 160 m (525 ft) from foundation. It is 550 m (1,804 ft) long and has a fill volume of 12,000,000 m³ (15,695,407 cu yd). The reservoir withheld by the dam, Lac de Grand Maison, has a storage capacity of 140,000,000 m³ (113,500 acre⋅ft). The power generation process begins with water stored in its reservoir at an altitude of 1,698 m (5,571 ft). By means of a 7,100 m (23,294 ft) long head-race tunnel which splits into three 1,450 m (4,757 ft) long penstocks, water is sent down to the power station. It is located on the rear bank of Lac du Verney at 45°08′43″N 06°03′03″E / 45.14528°N 6.05083°E / 45.14528; 6.05083 (Grand'Maison Power Plant) which lies at an elevation of 770 m (2,526 ft). The power station has above-ground and below-ground levels. On the above-ground level, there are four 150 MW Pelton turbine-generators which are used for normal conventional hydroelectric power generation. The below-ground level contains eight 150 MW Francis pump turbines which can be used for both power generation and pumping. After electricity is generated, the water is discharged into Lac du Verney, the lower reservoir. When storage in Grand'Maison needs to be replenished, the turbines reverse into pumps and move water from Lac du Verney back to the Grand'Maison Reservoir. The change in elevation between the reservoirs afford the above-ground station a maximum hydraulic head of 920 m (3,018 ft) and the below-ground station 955 m (3,133 ft).
The power station repeats the pumped-storage process as needed and acts as a peaking power plant. Power generation or pumping can be initiated within minutes. On an annual basis, the power station generates 1,420 GWh of electricity and consumes 1,720 GWh in pumping mode. Because pumping occurs during periods of low demand when electricity is cheaper than power generation during those of high demand, the power station is profitable.
Text imported from Wikipedia article "Grand''Maison Dam" and modified on July 23, 2019 according to the CC-BY-SA 4.0 International license.
Participants
Relevant Web Sites
Relevant Publications
- Le barrage de Grand'Maison. In: Travaux, n. 586 (March 1984), pp. 81-83.
- (1982): Le barrage et l'aménagement de Grand'Maison. In: Travaux, n. 564 (March 1982), pp. 36-45.
- (1982): Le chantier de construction du barrage de Grand'Maison. In: La Houille Blanche, v. 68, n. 5-6 (September 1982), pp. 487-495.
- (1982): Construction des barrages de Grand'Maison et du Verney. Equipement en matériels et maintenance. In: Travaux, n. 566 (May 1982), pp. 79-86.
- (1984): Le matériel sur le barrage de Grand'Maison. In: Travaux, n. 586 (March 1984), pp. 78-80.
- About this
data sheet - Structure-ID
20003771 - Published on:
22/06/2002 - Last updated on:
29/07/2014