General Information
| Name in local language: | Duomo di Napoli; Cattedrale di Santa Maria Assunta; Cattedrale di San Gennaro |
|---|---|
| Other name(s): | San Gennaro Cathedral |
| Completion: | 13th century |
| Status: | in use |
Project Type
| Function / usage: |
Cathedral |
|---|---|
| Material: |
Masonry structure |
| Structure: |
Dome |
| Architectural style: |
Gothic Baroque |
Awards and Distinctions
| 1940 |
for registered users |
|---|
Location
| Location: |
Naples, Napoli, Campania, Italy |
|---|---|
| Address: | Via Duomo 147 |
| Coordinates: | 40° 51' 9" N 14° 15' 34.56" E |
Technical Information
There currently is no technical data available.
Excerpt from Wikipedia
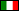
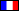
Naples Cathedral (Italian:Duomo di Napoli, Cattedrale di Santa Maria Assunta or Cattedrale di San Gennaro; Neapolitan:Viscuvato 'e Napule) is a Roman Catholic cathedral, the main church of Naples, southern Italy, and the seat of the Archbishop of Naples. It is widely known as the Cattedrale di San Gennaro, in honour of Saint Januarius, the city's patron saint.
History
The present cathedral was commissioned by King Charles I of Anjou. Construction continued during the reign of his successor, Charles II (1285-1309) and was completed in the early 14th century under Robert of Anjou. It was built on the foundations of two palaeo-Christian basilicas, whose traces can still be clearly seen. Underneath the building excavations have revealed Greek and Roman artifacts.
The Archbishop's Palace adjoins the cathedral.
Interior and artwork
The main attraction of the interior is the Royal Chapel of the Treasure of San Gennaro, with frescoes by Domenichino and Giovanni Lanfranco, altarpieces by Domenichino, Massimo Stanzione and Jusepe Ribera, the rich high altar by Francesco Solimena, the bronze railing by Cosimo Fanzago and other artworks, including a reliquary by 14th-century French masters.
Other artworks include an Assumption by Pietro Perugino, canvasses by Luca Giordano and the palaeo-Christian baptistery, with mosaics from the 4th century. The main chapel is a restoration of the 18th century, with a Baroque relief by Pietro Bracci. The Minutolo Chapel, mentioned in Boccaccio's Decameron, has 14th-century frescoes.
The crypt is by the Lombard Tommaso Malvito. The façade was reworked by Enrico Alvino in the late 19th century, but retains the 15th century portal, including some sculptures by Tino da Camaino.
Miracle of the Blood
The church houses a vial of the blood of Saint Januarius which is brought out three times a year, on the first Saturday in May, on 19 September and 16 December, when the dried blood usually liquefies. If the blood fails to liquefy, then legend has it that disaster will befall Naples.
A recent hypothesis by Garlaschelli, Ramaccini, and Della Sala is that the vial contains a thixotropic gel, he also explained on the Blood Miracle of Riddles of the Dead series on National Geographic Channel. In such a substance viscosity increases if left unstirred and decreases if stirred or moved. Researchers have proposed specifically a suspension of hydrated iron oxide, FeO(OH), which reproduces the color and behavior of the 'blood' in the ampoule. The suspension can be prepared from simple chemicals that would have been easily available locally since antiquity. On March 21, 2015, the blood in the vial appeared to liquify during a visit by Pope Francis. This was taken as a sign of the saint's favour of the pope. The blood did not liquify when Pope Benedict XVI visited in 2007.
Text imported from Wikipedia article "Naples Cathedral" and modified on June 3, 2020 according to the CC-BY-SA 4.0 International license.
Participants
Currently there is no information available about persons or companies having participated in this project.
Relevant Web Sites
Relevant Publications
- (1993): Strengthening of the Minutolo Chapel in Naples Cathedral. Presented at: IABSE Symposium: Structural Preservation of the Architectural Heritage, Rome, Italy, 1993.
- About this
data sheet - Structure-ID
20016955 - Published on:
22/07/2005 - Last updated on:
28/05/2021