General Information
| Completion: | 23 May 1967 |
|---|---|
| Status: | in use |
Project Type
| Function / usage: |
Commuter rail network |
|---|
Location
| km | Name |
Technical Information
Dimensions
| number of stations | 68 | |
| system length | 526 km | |
| track gauge | 1 435 mm | |
| number of lines | 7 |
Excerpt from Wikipedia
GO Transit rail services are provided throughout the Greater Toronto and Hamilton Area (GTHA) and the Greater Golden Horseshoe. The GO Transit rail fleet consists of 90 MPI MP40 locomotives and 979 Bombardier BiLevel Coaches. In 2023, the system had a ridership of 40,807,100 passengers per year. GO Transit started on May 23, 1967, running single-deck trains powered by diesel locomotives in push-pull configuration on a single rail line along Lake Ontario's shoreline. When GO trains began operation, they ran on tracks mostly owned the two major freight railways of Canada: Canadian National (CN) and CPKC. Over time, GO Transit (and subsequently Metrolinx) have acquired tracks, ensuring GO Transit has control over track maintenance and expansion. Metrolinx currently owns 80% of the GO's rail corridors.
All GO Transit fares are calculated by the fare zones that the origin and destination of the trip are in, as well as by passenger category (adult, student, senior or child). GO train fares are not differentiated based whether or not buses are used for part of the trip.
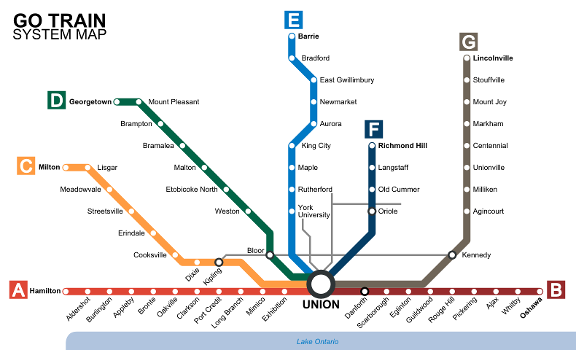
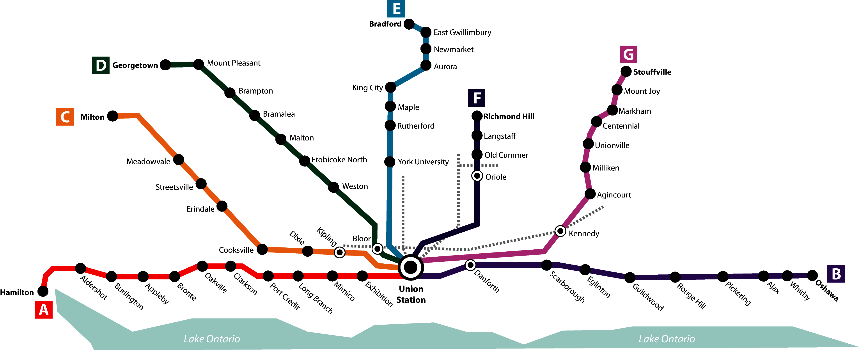
Lines and stations
History
GO Transit rail service began on May 23, 1967, on a single rail line along Lake Ontario's shoreline. GO Train service ran throughout the day from Oakville to Pickering with limited rush hour train service to Hamilton. This line, now divided as the Lakeshore East and Lakeshore West lines is the keystone corridor of GO Transit, and continued to be its only rail line for its first seven years of operation. GO's other five lines were opened between 1974 and 1982, significantly expanding the rail network from 86 to 332 kilometres long, and from 16 to 43 stations.
To that point, all of GO's rail services ran on tracks mostly owned by the two major freight railways of Canada: Canadian National (CN) and Canadian Pacific (CP). in 1988, a small but significant milestone in network growth occurred when it expanded its Lakeshore East line on new track it built by itself. But following that, the network experienced two long distance extensions to southern Barrie and Guelph in 1990, only to have those extensions reversed three years later. GO did extend its Lakeshore East line again in 1995 from Whitby to Oshawa, finishing that line as it exists today.
The reach of GO's network remained relatively unchanged between 1996 and 2005. However, seven new infill stations were opened along the Bradford and Stouffville lines. This coincided with GO's initial purchases of the rail corridors it operated on, taking ownership of the entire Stouffville line past Scarborough station, and most of the Barrie line north of the Toronto border. In addition, GO took control of the critical Union Station Rail Corridor, which all GO trains on all lines used. By the end of 2005, GO owned over a third of its rail network.
From 2007 to 2017, GO's network saw six extensions, requiring the Bradford line to be renamed as the "Barrie line", and the Georgetown line to "Kitchener line." These long distance extensions, along with the other extensions on the Lakeshore West, Richmond Hill and Stouffville lines, expanded GO's network length by 29%. Six critical corridor purchases were also made, tripling its length of owned corridors and bringing its ownership percentage to over 80%. Finally, 10 new stations were added, one of which coincided with the opening of the Toronto-York Spadina Subway Extension, creating a new interchange between GO and the TTC subway.
Future extensions
Lakeshore East to Bowmanville
A 20km extension of the Lakeshore East line to Bowmanville was announced by then-premier Kathleen Wynne in 2016. Construction began on July 22, 2024 and is not expected to finish for years. No completion date has been provided. The extension is expected to cost $730 million, and will provide two-way all day service. The line will travel upwards from the current Oshawa GO station and continue along the CPKC corridor to Bowmanville, adding four more stations, Thornton's Corners East, Ritson, Courtice, and Bowmanville.
Future improvements
Two-way all day service on the Milton line
The Milton line is owned and operated by Canadian Pacific Kansas City which has restricted the number of passenger trains, only allowing for one-way service. In 2024, the Ontario government under Doug Ford called on the federal government to share the cost of construction for two-way all day service on the Milton line. The project would involve a complete separation from CPKC's tracks by building dedicated GO Transit tracks along the rail corridor, and is estimated to be at $6 billion dollars. No timeline has been provided, and construction has not yet started.
GO train electrification
In 2010, then-premier Kathleen Wynne announced plans to electrify GO Transit. Electrification would drastically cut down on GO Transit's carbon emissions and would allow GO Transit to run faster, more frequent trains, increasing ridership. In 2018, it was decided to use an overhead wire system over a third rail. Hydrogen fuel cells were studied as an alternative to rail electrification but ultimately were deemed unfeasible. A report suggested the trains would be 30% faster and 60% cheaper per kilometre. In 2022, the Ontario government under premier Doug Ford began the first phase of electrification, with plans to electrify 600 kilometres of track and an estimated finish date of 2032.
Future lines
Bolton line
GO Transit rail service to Bolton was first proposed by the Ontario government under the MoveOntario 2020 plan in June 2007. It was subsequently carried over to The Big Move, where it was placed on the 15-year plan. In November 2010, Metrolinx completed a feasibility study that focused on utilization of Canadian Pacific Railway's Mactier subdivision, which runs from the West Toronto Diamond in Toronto northward to Bolton. Four different service alternatives were assessed to determine the best method to carry passengers into Toronto from the Mactier subdivision, and the preferred option was to direct trains east-west along CN's Halton subdivision, and north-south again along GO Transit's existing Barrie line. This would provide four new stations in the communities of Woodbridge and Kleinburg in the City of Vaughan, and Bolton in the Town of Caledon, and also use the existing Downsview Park station before terminating at Union.
The feasibility study estimated that minimum infrastructure costs were $160 million for peak direction rush-hour service, and resulting ridership was forecasted to be 2,391, 2,884, and 4,388 in 2015, 2021, and 2031, respectively, in the morning peak period. If service was increased for two-way all-day service, total costs increased to $210 million, and ridership was forecasted to be 6,074, 7,324, and 11,146 in 2015, 2021, and 2031, respectively. Metrolinx determined that the projected ridership did not justify the costs, and downgraded the Bolton line from the 15- to the 25-year plan on February 14, 2013, when amendments were made to The Big Move.
Midtown corridor and Peterborough line
The Midtown corridor refers to three new GO Transit services in The Big Move. The first is a Crosstown line from Dundas Street to the former CP North Toronto and Leaside stations in Toronto. The second and third segments would extend east from North Toronto and/or Union Station: the Seaton line to Seaton, and the Locust Hill line to Locust Hill.
GO Transit has contemplated a Midtown corridor since the 1980s as a contingency plan once capacity at Union Station became constrained, making North Toronto an alternate station for Downtown Toronto. The major barrier to these plans, however, is the fact that the Midtown corridor is composed of existing rail lines owned and actively used by the CPKC as its main freight line between Ottawa, Montreal, London and Windsor. CPKC has been reluctant to provide capacity to GO Transit on its tracks, and the Milton line (which runs along CPKC tracks to the west) only came after considerable negotiations, the 1979 Mississauga train derailment, and an investment of hundreds of millions of dollars.
All three lines in the corridor were listed under the 15-year plan of The Big Move upon its publication in 2008. However, the Havelock line was moved to the 25-year plan on February 14, 2013, because of "very modest ridership potential and significant infrastructure and operational challenges related to the Agincourt rail yards."
Via Rail provided train service to Peterborough until 1990, when service was cancelled. The potential to provide commuter rail service to Peterborough was noted by GO Transit in its 2020 strategic plan, and was also included in The Big Move. Metrolinx completed a study for bringing commuter rail service to Peterborough in February 2010. Different routes were explored, all of which use CPKC's existing Havelock subdivision between Peterborough and Toronto. Once reaching Toronto, three different routes were explored through the east end, to deal with the same "significant infrastructure and operational challenges related to the Agincourt rail yards" that complicate GO's Havelock line. The study also kept the option open of using either Union Station or North Toronto station as the terminus of the line. Capital costs to upgrading the Havelock subdivision were estimated to be between C$329 and 384 million. GO introduced bus service between Peterborough and Oshawa on September 5, 2009.
Cambridge-Guelph rail link
Proposals from regional councillors have pushed for a rail link between Cambridge and Guelph operated by Metrolinx, with an estimated 14 to 17 minute travel time and frequency of every 30 to 60 minutes. The line would be built along a Canadian National spur between the two cities. Reports have forecasted a ridership of over 500,000 by 2041, and would cut travel time between Cambridge and Union Station to 87 minutes.
Text imported from Wikipedia article "GO Transit rail services" and modified on January 20, 2025 according to the CC-BY-SA 4.0 International license.
Participants
Currently there is no information available about persons or companies having participated in this project.
Relevant Web Sites
- About this
data sheet - Structure-ID
20090340 - Published on:
19/01/2025 - Last updated on:
19/01/2025