General Information
| Name in local language: | Γεφύρι της Άρτας |
|---|---|
| Completion: | 1612 |
| Status: | in use |
Project Type
| Structure: |
Semi-circular arch bridge |
|---|---|
| Function / usage: |
Pedestrian bridge (footbridge) |
| Material: |
Masonry bridge |
| Architectural style: |
Ottoman |
| Material: |
Structurae Plus/Pro - Subscribe Now! |
Location
| Location: |
Arta, Arta, Epirus, Greece |
|---|---|
| Crosses: |
|
| Near: |
Arta Bridge
|
| Coordinates: | 39° 9' 6" N 20° 58' 28" E |
Technical Information
Dimensions
| height | 12.50 m | |
| total length | 130 m | |
| span lengths | 24.00 m - 15.80 m - 15.40 m - 15.20 m | |
| number of spans | 4 |
Materials
| arches |
stone
|
|---|
Excerpt from Wikipedia
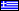
The Bridge of Arta (Greek: Γεφύρι της Άρτας) is a stone bridge that crosses the Arachthos river (Άραχθος) in the west of the city of Arta (Άρτα) in Greece. It has been rebuilt many times over the centuries, starting with Roman or perhaps older foundations; the current bridge is probably a 17th-century Ottoman construction.
The folk ballad "The Bridge of Arta" tells a story of human sacrifice during its building. From the ballad, a number of Greek proverbs and customary expressions arose, associated with interminable delays, as in the text of the ballad: "All day they were building it, and in the night it would collapse."
History
According to the Epirote chronicler Panayiotis Aravantinos, the bridge was first built under the Roman Empire. Some traditions say it was rebuilt when Arta became capital of the Despotate of Epirus, possibly under Michael II Doukas (r. 1230–1268). The current bridge is Ottoman, probably from 1602–06 or perhaps 1613. From the annexation of Arta in 1881 to the outbreak of the First Balkan War in 1912, the highest point of the bridge was the border between the Ottoman Empire and the Kingdom of Greece.
Folklore
According to the folk ballad of the acritic songs family, 45 masons and 60 apprentices, under the leadership of the Head Builder, were building a bridge, but its foundations would collapse each night. Finally a bird with a human voice informed the Head Builder that, in order for the bridge to remain standing, he should sacrifice his wife. As she is being buried alive in the foundations of the construction, she curses the bridge to flutter like a leaf, and those who pass it to fall like leaves also. She is then reminded that her brother is abroad and might pass the bridge himself, so she changes her curses so as to become actual blessings: "As the tall mountains tremble, so shall the bridge tremble, and as the birds of prey fall, so shall passers fall".
Parallels
The idea that a major edifice cannot be built without a human sacrifice ("inbuilding" of a person) was also common in the folklore of other Balkan peoples such as Bulgarians, Albanians, Serbs and Romanians; for example, the Romanian legend of Meşterul Manole. A masterbuilder being forced to sacrifice his wife in this way is a common theme in folk songs. A recurring plot element is the masterbuilders' decision to sacrifice the woman who comes first to the building site to bring them food. All but one break their promise and tell their wives to come late, and it is the wife of the only honest one that is sacrificed.
One of the legends associated with Merlin is that Vortigern, the King of the Celts, was building a tower to defend himself from Ambrosius and Uther Pendragon. Like the Bridge of Arta, whenever they finished one day's work on the tower it would collapse in the night and Vortigern's advisors recommended that sacrificing a child and mixing his blood with the mortar would prevent the collapse.
Text imported from Wikipedia article "Bridge of Arta" and modified on May 26, 2020 according to the CC-BY-SA 4.0 International license.
Participants
Currently there is no information available about persons or companies having participated in this project.
Relevant Web Sites
Relevant Publications
- (1984): Buiding bridges. History, Technology, Construction. Beton-Verlag, Düsseldorf (Germany).
- (1990): Les grands ponts du monde: Ponts remarquables d'Europe. Brissaud, Poitiers (France), pp. 287.
- (1999): Le Passage. 1st edition, Everest Communication, Luxembourg (Luxembourg), pp. 96-99.
- (2005): Stone footbridges in Greece. Presented at: Footbridge 2005 (Second International Congress), Venezia, 06-08 December 2005.
- (1999): Tierra sobre el agua. Visión histórica universal de los puentes. Colegio de Ingenieros de Caminos, Canales y Puertos, Madrid (Spain), pp. 150.
- About this
data sheet - Structure-ID
20000662 - Published on:
09/04/2000 - Last updated on:
28/05/2021