The Osabe Viaduct: Long service life thanks to installed Monitoring System
The Osabe Viaduct was built as a part of the reconstruction project of the Sanriku Coast Road (National Highway 45) near the town of Rikuzentakata in the Iwate Prefecture in Japan. Due to the serious damage that was caused by the “Great East Japan Earthquake” in 2011, the new Sanriku Coast Road is constructed at a higher elevation than the existing road in order to minimize damage that may be caused by future tsunamis.
The Osabe Viaduct is a six-span, prestressed concrete continuous rigid frame box girder bridge. Since the bridge is located in the cold north of Japan, it is exposed to detrimental influences such as freezing and de-icing salts. Consequently, a number of new construction methods were implemented to enhance the bridge’s durability.
Permanent magnets measure tension force
“SmART Cell Sensors” were used to measure and confirm the prestressing force acting in the bridge girder. In this system, permanent magnets measure the tension force of a strand by measuring the changes in the magnetic properties that occur during the tensioning of the strand.
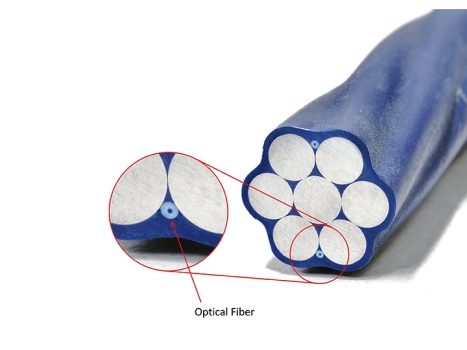
Strands with optical fibres
Furthermore, epoxy coated and filled strands with optical fibres were used. The strand provides strain data for itself when it is stressed. This data can be converted to the tensile force of a cable using the E-modulus. The special strands were used for the inner post-tensioning tendons, and the data measured during stressing was used for stressing management. Using this technique, the forces acting on the structure can also be measured at any time in the future.
New technique for concrete curing
A highly water-repellent sheet was used as a new technique for concrete curing. This sheet is attached to the inside face of the forms and kept in place during concrete pouring. The sheet is kept in contact with the concrete surface even after the removal of forms in order to extend the time of curing for as long as possible. This method perfectly controls the loss of moisture in the concrete by leaving the sheet in contact with the concrete surface and preventing it from direct exposure to ambient air. This method not only reduces surface voids, but also improves salt insulation properties and the neutralization resistance of the concrete. Furthermore, it suppresses the concrete drying shrinkage strain.
Multiple corrosion protection methods
To improve the durability of the tendons and anchorages, multiple corrosion protection methods were selected. Type 19S15.2 MC DYWIDAG epoxy coated strand tendons with HDPE sheathed strands were used as external post-tensioning tendons with double layered corrosion protection.
Cement grouted epoxy coated strand tendons with HDPE sheathed strands were installed as internal post-tensioning tendons with triple corrosion protection. Pre-grouted strand tendons with double corrosion protection were used for transverse post-tensioning. In addition, the steel members of each anchorage were coated with a thick layer of electrostatic epoxy resin powder coating to improve corrosion resistance.
Structure Types
- About this
data sheet - Product-ID
7634 - Published on:
20/05/2019 - Last updated on:
17/11/2021