Design Expressions for the Effective Width of Composite Steel-Concrete Members
|
|
|||||||||||
Bibliographic Details
| Author(s): |
Fabrizio Gara
Gianluca Ranzi Graziano Leoni |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium: | conference paper | ||||
| Language(s): | English | ||||
| Conference: | IABSE Symposium: Engineering for Progress, Nature and People, Madrid, Spain, 3-5 September 2014 | ||||
| Published in: | IABSE Symposium Madrid 2014 | ||||
|
|||||
| Page(s): | 161-168 | ||||
| Total no. of pages: | 8 | ||||
| Year: | 2014 | ||||
| DOI: | 10.2749/222137814814027701 | ||||
| Abstract: |
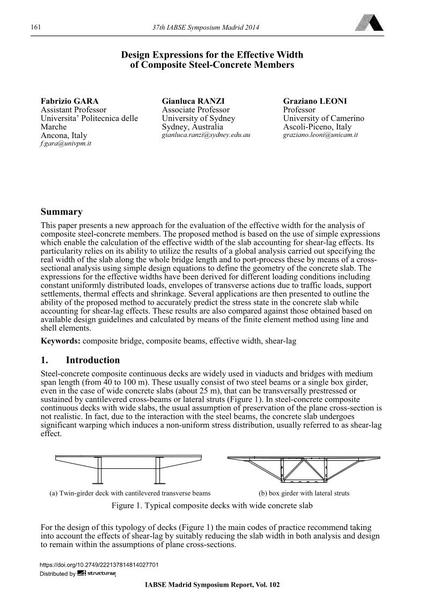
This paper presents a new approach for the evaluation of the effective width for the analysis of composite steel-concrete members. The proposed method is based on the use of simple expressions which enable the calculation of the effective width of the slab accounting for shear-lag effects. Its particularity relies on its ability to utilize the results of a global analysis carried out specifying the real width of the slab along the whole bridge length and to port-process these by means of a cross- sectional analysis using simple design equations to define the geometry of the concrete slab. The expressions for the effective widths have been derived for different loading conditions including constant uniformly distributed loads, envelopes of transverse actions due to traffic loads, support settlements, thermal effects and shrinkage. Several applications are then presented to outline the ability of the proposed method to accurately predict the stress state in the concrete slab while accounting for shear-lag effects. These results are also compared against those obtained based on available design guidelines and calculated by means of the finite element method using line and shell elements. |
||||
| Keywords: |
composite bridge effective width composite beams shear-lag
|
||||
