Design of Deep Beams with Openings using Strut-and-Tie Models
The Importance of Detailing and Spreading Reinforcement
|
|
|||||||||||
Bibliographic Details
| Author(s): |
David Birrcher
Insung Kim John Breen |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium: | conference paper | ||||
| Language(s): | English | ||||
| Conference: | 17th IABSE Congress: Creating and Renewing Urban Structures – Tall Buildings, Bridges and Infrastructure, Chicago, USA, 17-19 September 2008 | ||||
| Published in: | IABSE Congress Chicago 2008 | ||||
|
|||||
| Page(s): | 566-567 | ||||
| Total no. of pages: | 8 | ||||
| Year: | 2008 | ||||
| DOI: | 10.2749/222137908796293884 | ||||
| Abstract: |
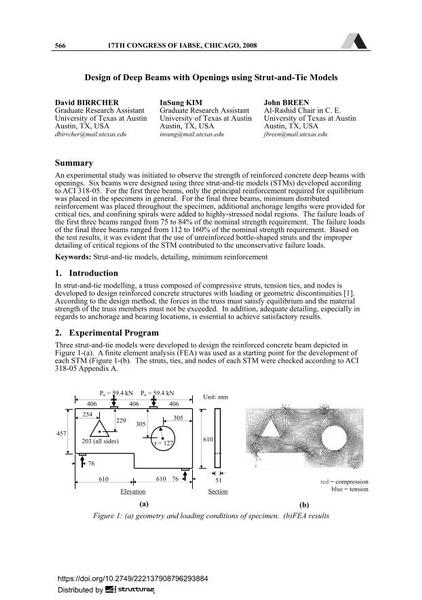
An experimental study was initiated to observe the strength of reinforced concrete deep beams with openings. Six beams were designed using three strut-and-tie models (STMs) developed according to ACI 318-05. For the first three beams, only the principal reinforcement required for equilibrium was placed in the specimens in general. For the final three beams, minimum distributed reinforcement was placed throughout the specimen, additional anchorage lengths were provided for critical ties, and confining spirals were added to highly-stressed nodal regions. The failure loads of the first three beams ranged from 75 to 84% of the nominal strength requirement. The failure loads of the final three beams ranged from 112 to 160% of the nominal strength requirement. Based on the test results, it was evident that the use of unreinforced bottle-shaped struts and the improper detailing of critical regions of the STM contributed to the unconservative failure loads. |
||||
| Keywords: |
strut-and-tie models detailing minimum reinforcement
|
||||
