Seismic design of traditional wooden five-storied pagoda
|
|
|||||||||||
Bibliographic Details
| Author(s): |
Norikazu Ikema
Kimihiko Morita Masayasu Matsubara |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium: | conference paper | ||||
| Language(s): | English | ||||
| Conference: | 17th IABSE Congress: Creating and Renewing Urban Structures – Tall Buildings, Bridges and Infrastructure, Chicago, USA, 17-19 September 2008 | ||||
| Published in: | IABSE Congress Chicago 2008 | ||||
|
|||||
| Page(s): | 190-191 | ||||
| Total no. of pages: | 6 | ||||
| Year: | 2008 | ||||
| DOI: | 10.2749/222137908796292191 | ||||
| Abstract: |
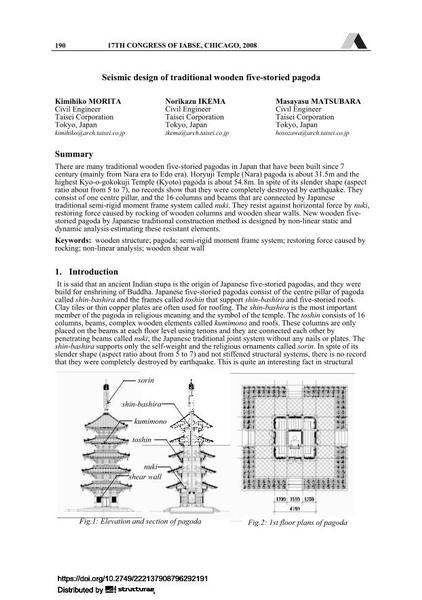
There are many traditional wooden five-storied pagodas in Japan that have been built since 7 century (mainly from Nara era to Edo era). Horyuji Temple (Nara) pagoda is about 31.5m and the highest Kyo-o-gokokuji Temple (Kyoto) pagoda is about 54.8m. In spite of its slender shape (aspect ratio about from 5 to 7), no records show that they were completely destroyed by earthquake. They consist of one centre pillar, and the 16 columns and beams that are connected by Japanese traditional semi-rigid moment frame system callednuki. They resist against horizontal force bynuki, restoring force caused by rocking of wooden columns and wooden shear walls. New wooden five- storied pagoda by Japanese traditional construction method is designed by non-linear static and dynamic analyses estimating these resistant elements. |
||||
| Keywords: |
wooden structure non-linear analysis pagoda semi-rigid moment frame system restoring force caused by rocking wooden shear wall
|
||||

